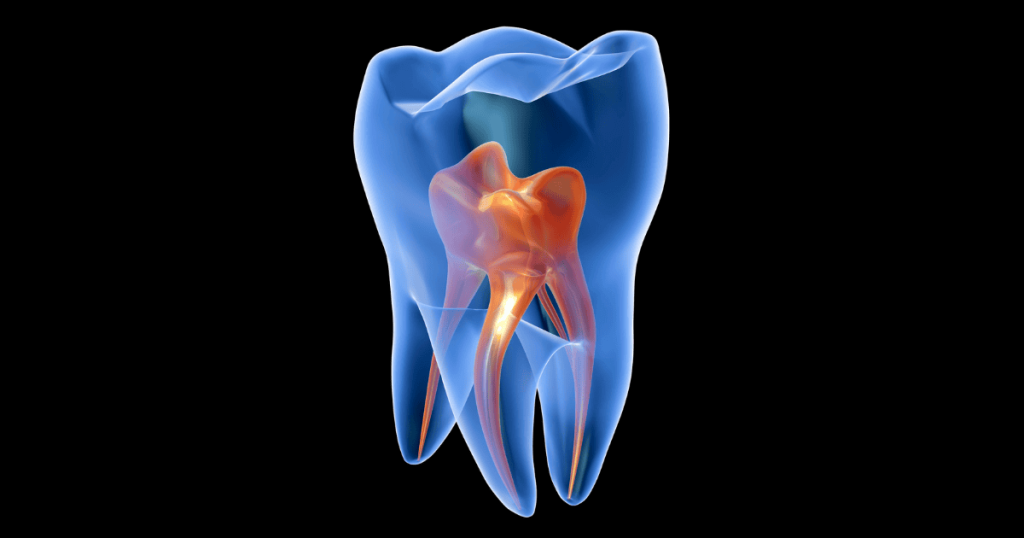
Understanding How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You: Timeline and Risks

A tooth infection, often called a dental abscess, can become life-threatening if left untreated. Understanding “how long until a tooth infection kills you” is crucial. Initially causing mild discomfort or a persistent toothache, these infections can quickly escalate, spreading to the gums, face, or neck.
Without timely treatment, severe symptoms like swelling, difficulty swallowing, and fever may develop. Prompt dental care is essential to prevent complications such as sepsis or Ludwig’s angina, which can lead to serious health issues or even death.
Introduction
A tooth infection may start innocuously with slight discomfort or mild pain but can rapidly develop into a potentially life-threatening situation.
Understanding the progression and dangers of tooth infections is crucial for maintaining oral health and overall well-being.
What is a Tooth Infection?

Let’s delve into this article to understand more about what a tooth infection is and how it relates to “how long until a tooth infection kills you.
Definition and Types
A tooth infection occurs when bacteria invade the dental pulp—the innermost part of the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels. This can happen due to untreated cavities, dental trauma, or advanced gum disease. There are different types of tooth infections:
- Periapical Abscess: This occurs at the tip of the tooth’s root due to untreated cavities.
- Periodontal Abscess: This forms in the gums alongside a tooth’s root, often due to gum disease.
- Gingival Abscess: This develops in the gums and is typically caused by foreign objects or food particles lodged in the gums.
Causes of Tooth Infections
Tooth infections primarily result from poor dental hygiene practices, untreated dental issues such as cavities, or trauma to the tooth.
Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a tooth infection early is crucial for seeking timely treatment and preventing complications.
Early Signs
- Persistent Toothache: A continuous, throbbing pain in the affected tooth or surrounding area.
- Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, which can indicate nerve involvement.
- Swelling: Swelling in the gums, face, or neck around the affected tooth.
- Redness: Red or inflamed gums that may be tender to touch.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath despite regular oral hygiene practices.
Severe Symptoms
As the infection progresses, more severe symptoms may develop, indicating a spreading infection:
- Fever: A high fever, indicating the body is fighting a systemic infection.
- Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing: Swelling in the face or neck can obstruct airways, making it challenging to swallow or breathe.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Tender, swollen lymph nodes in the neck or under the jaw.
- Pus Drainage: Pus may drain from the infected area, causing a foul taste in the mouth.
- Facial Swelling: Noticeable swelling in the face, particularly around the eyes, cheeks, or jawline.

Dangers and Complications of Untreated Tooth Infections
Ignoring or delaying treatment for a tooth infection can lead to severe health complications.
Potential Health Risks
- Sepsis: The infection can spread through the bloodstream, causing systemic inflammation and potentially leading to organ failure.
- Ludwig’s Angina: A severe infection of the floor of the mouth that can cause significant swelling, obstructing the airway.
- Brain Abscess: If the infection reaches the brain, it can lead to a brain abscess, causing neurological symptoms and requiring urgent medical intervention.
- Osteomyelitis: An infection of the bone surrounding the tooth, which can result in bone death and further complications.
- Endocarditis: Bacteria from the dental infection can enter the bloodstream and attach to damaged areas of the heart’s lining, leading to an infection of the heart valves.
Potential Dangers of Untreated Tooth Infections
Neglecting treatment for a tooth infection can have serious health consequences. It’s important to recognize the risks associated with untreated dental abscesses to safeguard your oral and overall well-being.
Understanding how long until a tooth infection kills you highlights the urgency of seeking prompt dental care to prevent severe complications.
How Quickly Can a Tooth Infection Become Dangerous?
The timeline for a tooth infection to become life-threatening varies based on factors such as the individual’s overall health, the severity of the infection, and the promptness of treatment.
Understanding how long until a tooth infection kills you is crucial, as it emphasizes the importance of seeking immediate dental care to prevent severe complications.
Timeline of Infection Progression
- Initial Infection (Days to Weeks): The infection begins in the dental pulp, causing pain and swelling. Without treatment, it can spread to nearby tissues.
- Spreading Infection (Weeks): Left untreated, the infection can extend to the jaw, face, and neck, leading to more severe symptoms like difficulty swallowing and breathing.
- Severe Complications (Weeks to Months): In severe cases, the infection can spread systemically, causing conditions like sepsis that can progress rapidly.
Factors Influencing Infection Speed
Several factors influence how quickly a tooth infection can become dangerous:
- Immune System Health: A weakened immune system may allow the infection to spread more rapidly.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes can impair healing and increase infection risks.
- Access to Dental Care: Timely access to dental treatment can prevent infection escalation.
Treatment Options for Tooth Infections
Prompt and appropriate treatment is essential to prevent complications associated with tooth infections.
Immediate Steps
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers can alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics: Dentists may prescribe antibiotics to control the infection, especially if it has started to spread.
Medical Treatments

- Drainage: If an abscess is present, drainage may be necessary to relieve pressure and eliminate the infection.
- Root Canal Treatment: This procedure involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning the interior of the tooth, and sealing it to prevent reinfection.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases where the tooth cannot be saved, extraction may be necessary to prevent infection spread.
Post-Treatment Care
- Follow-up Visits: Regular check-ups are essential to ensure the infection is fully resolved and prevent recurrence.
- Oral Hygiene Practices: Maintain good oral hygiene, including brushing twice daily and flossing, to prevent future infections.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Eat a balanced diet, stay hydrated, and avoid tobacco use to support overall health and dental well-being.
Prevention Tips for Tooth Infections
Preventing tooth infections starts with proactive oral hygiene and regular dental care.
Maintaining Oral Hygiene
- Brushing: Brush teeth twice daily using fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing: Clean between teeth daily with dental floss or interdental cleaners.
- Mouthwash: Use antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and maintain oral freshness.
Regular Dental Visits
- Check-ups: Visit your dentist biannually for routine examinations and professional cleanings.
- Early Intervention: Address dental issues promptly, such as cavities or gum disease, to prevent infection.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Diet: Consume a nutritious diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support dental health.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to flush out food particles and bacteria.
- Avoid Tobacco: Refrain from smoking or using tobacco products, as they increase the risk of gum disease and dental infections.
Conclusion
A tooth infection is more than just a dental problem—it’s a serious health issue that needs urgent attention. Understanding the symptoms, risks, and treatment options outlined in this article is crucial to protect yourself from serious complications.
If you observe any signs of a tooth infection, don’t wait—seek prompt, professional dental care to protect your health and well-being. Understanding how long until a tooth infection kills you underscores the importance of timely intervention and proactive dental health management.
FAQs About How Long Until A Tooth Infection Kills You?
Common signs include persistent toothache, swelling, sensitivity, bad breath, and fever. If you experience these symptoms, consult a dentist promptly.
No, tooth infections require professional treatment. Without intervention, they can worsen and lead to severe complications.
Antibiotics typically begin to alleviate symptoms within a few days. Completing the full course as prescribed is crucial for effective treatment.
Yes, especially if symptoms like severe pain, swelling, or difficulty breathing occur. Immediate dental care is necessary to prevent complications.